Apr 03, 2018 Written by Anurag Pant Exposure

EXPOSURE
1.exposure is the amount of light per unit area (the image plane luminance times the exposure time) reaching a photographic film or electronic image sensor as determined by shutter speed, lens aperture and scene luminance.
2. "exposure" is simply an image that is captured in one single opening and closing of the shutter.
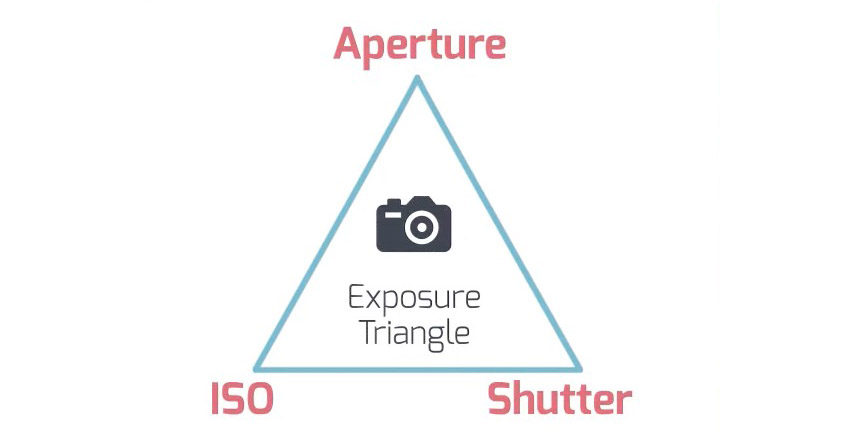
3. In exposure, there are three main ingredients or elements that work together: Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO.
4. The actual brightness of an exposure is measured in "stops" or EVs. Generally speaking, one EV or stop is an amount of light that is either twice as bright or half as bright as the current amount of light.
5. Exposure compensation is a camera function that allows you to brighten or darken your exposure by a specified amount while your camera is in any automatic exposure mode.
6. As a side note, most advanced cameras also allow you to dial in exposure compensation while in manual exposure mode as well, which can cause confusion.
7. If your shutter speed, aperture, and ISO are all under manual control, what EV compensation does is simply influence what your camera's light meter believes is a correct exposure.
8. The exposure is controlled by the camera's light meter. The light meter determines what the proper exposure is; it all sets the f-stop and shutter speed. The f-stop is a fraction; the f represents the focal length.
9. Exposure is a combination of the length of time and the illuminance at the photosensitive material. Exposure time is controlled in a camera by shutter speed, and the illuminance depends on the lens aperture and the scene luminance.
10. Slower shutter speeds (exposing the medium for a longer period of time) greater lens apertures (admitting more light) and higher-luminance scenes produce greater exposures.